Hive Source¶
Download connector Hive Source Connector for Kafka 2.1.0
Kafka Connect Hive is a Source Connector for reading data from Hive and writing to Kafka.
Prerequisites¶
- Apache Kafka 2.x or above
- Kafka Connect 2.x or above
- Hive
- Java 1.8
Features¶
- The KCQL routing querying - Allows for the table to topic routing
- Error policies for handling failures
- Payload support for Schema.Struct and payload Struct, Schema.String and JSON payload and JSON payload with no schema
KCQL Support¶
The KCQL (Kafka Connect Query Languages) is a SQL like syntax allowing a streamlined configuration of Kafka Connect Source. More details about KCQL can be found here.
INSERT INTO kafka_topic SELECT { FIELD, ... } FROM hive_table
Tip
You can specify multiple KCQL statements separated by ; to have a the connector sink multiple topics.
The Hive source supports KCQL:
- Field selection
- Selection of Hive source tables
- Selection of Kafka target topics.
Example:
-- Insert into kafka_topicA all fields from hive_tableA
INSERT INTO kafka_topicA SELECT * FROM hive_tableA
Payload Support¶
Schema.Struct and a Struct Payload¶
If you follow the best practice while producing the events, each message should carry its schema information. The best option is to send AVRO. Your Connector configurations options include:
key.converter=io.confluent.connect.avro.AvroConverter
key.converter.schema.registry.url=http://localhost:8081
value.converter=io.confluent.connect.avro.AvroConverter
value.converter.schema.registry.url=http://localhost:8081
This requires the SchemaRegistry.
Note
This needs to be done in the connect worker properties if using Kafka versions prior to 0.11
Schema.String and a JSON Payload¶
Sometimes the producer would find it easier to just send a message with
Schema.String and a JSON string. In this case your connector configuration should be set to value.converter=org.apache.kafka.connect.json.JsonConverter.
This doesn’t require the SchemaRegistry.
key.converter=org.apache.kafka.connect.json.JsonConverter
value.converter=org.apache.kafka.connect.json.JsonConverter
Note
This needs to be done in the connect worker properties if using Kafka versions prior to 0.11
No schema and a JSON Payload¶
There are many existing systems which are publishing Json over Kafka and bringing them in line with best practices is quite a challenge, hence we added the support. To enable this support you must change the converters in the connector configuration.
key.converter=org.apache.kafka.connect.json.JsonConverter
key.converter.schemas.enable=false
value.converter=org.apache.kafka.connect.json.JsonConverter
value.converter.schemas.enable=false
Note
This needs to be done in the connect worker properties if using Kafka versions prior to 0.11
Error Polices¶
The sink has three error policies that determine how failed writes to the target database are handled. These error polices allow you to control the behaviour of the sink if it encounters an error when writing records to the target system. Since Kafka retains the records, subject to the configured retention policy of the topic, the sink can ignore the error, fail the connector or attempt redelivery.
Throw
Any error on write to the target system will be propagated up and processing is stopped. This is the default behavior.
Noop
Any error on write to the target database is ignored and processing continues.
Warning
This can lead to missed errors if you don’t have adequate monitoring. Data is not lost as it’s still in Kafka subject to Kafka’s retention policy. The sink currently does not distinguish between integrity constraint violations and or other exceptions thrown by any drivers or target systems.
Retry
Any error on write to the target system causes the RetryIterable exception to be thrown. This causes the Kafka Connect framework to pause and replay the message. Offsets are not committed. For example, if the table is offline it will cause a write failure, the message can be replayed. With the Retry policy, the issue can be fixed without stopping the sink.
Lenses QuickStart¶
The easiest way to try out this is using Lenses Box the pre-configured docker, that comes with this connector pre-installed. You would need to Connectors –> New Connector –> Hive and paste your configuration
Source Connector QuickStart¶
Test Data¶
Once you have installed and started Hive create a database to extract records from. This snippet creates a table called hive_connect and inserts 3 rows representing cities data.
Start the Hive shell and execute the following:
hive> create database hive_connect;
hive> use hive_connect;
hive> create table cities (city string, state string, population int, country string) stored as parquet;
hive> insert into table cities values ("Philadelphia", "PA", 1568000, "USA");
insert into table cities values ("Chicago", "IL", 2705000, "USA");
insert into table cities values ("New York", "NY", 8538000, "USA");
The most important thing here is to store the data as parquet. Lets check the data is available to read.
select * from cities;
New York NY 8538000 USA
Chicago IL 2705000 USA
Philadelphia PA 1568000 USA
Time taken: 0.12 seconds, Fetched: 3 row(s)
Installing the Connector¶
Connect, in production should be run in distributed mode
- Install and configure a Kafka Connect cluster
- Create a folder on each server called
plugins/lib - Copy into the above folder the required connector jars from the stream reactor download
- Edit
connect-avro-distributed.propertiesin theetc/schema-registryfolder and uncomment theplugin.pathoption. Set it to the root directory i.e. plugins you deployed the stream reactor connector jars in step 2. - Start Connect,
bin/connect-distributed etc/schema-registry/connect-avro-distributed.properties
Connect Workers are long running processes so set an init.d or systemctl service accordingly.
Starting the Connector (Distributed)¶
Download, and install Stream Reactor to your Kafka Connect cluster. Follow the instructions here if you haven’t already done so. All paths in the quickstart are based on the location you installed Stream Reactor.
Once the Connect has started we can now use the kafka-connect-tools cli to post in our distributed properties file for Hive. If you are using the dockers you will have to set the following environment variable too for the CLI to connect to the Kafka Connect Rest API.
export KAFKA_CONNECT_REST="http://myserver:myport"
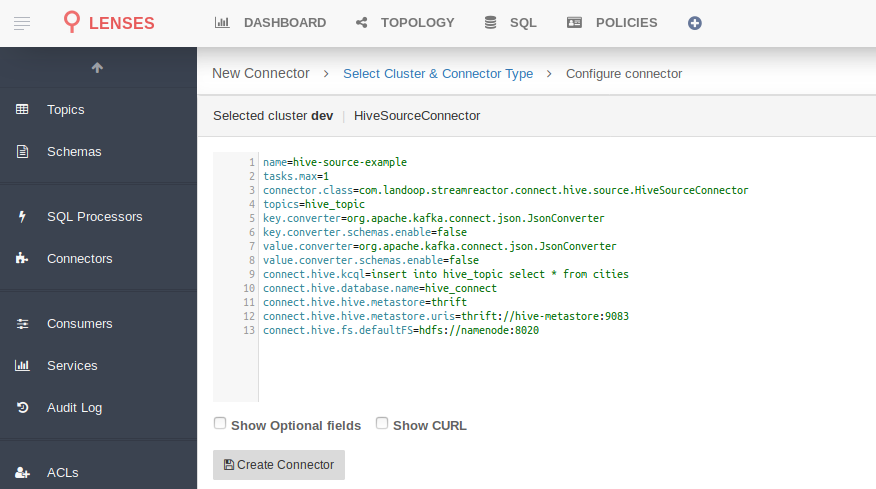
➜ bin/connect-cli create hive-source-example < conf/hive-source.properties
name=hive-source-example
connector.class=com.landoop.streamreactor.connect.hive.source.HiveSourceConnector
tasks.max=1
topics=hive_topic
key.converter=org.apache.kafka.connect.json.JsonConverter
key.converter.schemas.enable=false
value.converter=org.apache.kafka.connect.json.JsonConverter
value.converter.schemas.enable=false
connect.hive.kcql=insert into hive_topic select * from cities
connect.hive.database.name=hive_connect
connect.hive.hive.metastore=thrift
connect.hive.hive.metastore.uris=thrift://hive-metastore:9083
connect.hive.fs.defaultFS=hdfs://namenode:8020
We can use the CLI to check if the connector is up but you should be able to see this in logs as well.
#check for running connectors with the CLI
➜ bin/connect-cli ps
hive-source
INFO
__ ______ __ __ _____ ______ ______ ______ __ __ __ __ __ ______
/\ \ /\ __ \ /\ "-.\ \ /\ __-. /\ __ \ /\ __ \ /\ == \ /\ \_\ \ /\ \ /\ \ / / /\ ___\
\ \ \____ \ \ __ \ \ \ \-. \ \ \ \/\ \ \ \ \/\ \ \ \ \/\ \ \ \ _-/ \ \ __ \ \ \ \ \ \ \'/ \ \ __\
\ \_____\ \ \_\ \_\ \ \_\\"\_\ \ \____- \ \_____\ \ \_____\ \ \_\ \ \_\ \_\ \ \_\ \ \__| \ \_____\
\/_____/ \/_/\/_/ \/_/ \/_/ \/____/ \/_____/ \/_____/ \/_/ \/_/\/_/ \/_/ \/_/ \/_____/
Check for records in Kafka¶
Let’s see what was sent over to the hive_topic
➜ bin/kafka-avro-console-consumer \
--zookeeper localhost:2181 \
--topic hive-topic \
--from-beginning
{"id":{"int":1},"city":{"string":"Philadelphia"},"state":{"string":"PA"},"population":{"int":1568000},"country":{"string":"USA"}}
{"id":{"int":2},"city":{"string":"Chicago"},"state":{"string":"IL"},"population":{"int":2705000},"country":{"string":"USA"}}
{"id":{"int":3},"city":{"string":"New York"},"state":{"string":"NY"},"population":{"int":8538000},"country":{"string":"USA"}}
Kerberos¶
For those clusters using Kerberos for authentication, the connector supports two modes. Controlling the modes happens via connect.hive.security.kerberos.auth.mode configuration. The supported values are KEYTAB and USERPASSWORD. The connect.hive.security.kerberos.ticket.renew.ms configuration controls the interval (in milliseconds) to renew a previously obtained (during the login step) Kerberos token.
Keytab
When this mode is configured, these extra configurations need to be set:
connect.hive.security.principal= ....
connect.hive.security.keytab = /path/to/the/keytab
connect.hive.security.namenode.principal=....
The keytab file needs to be available on the same path on all the Connect cluster workers. In case the file is missing an error will be raised. You can find the details about the configurations in the Optional Configurations section.
Warning
The connector has been written to support multiple Kerberos principals within the same Connect worker
User-password
For those setups where a keytab is not available, the Kerberos authentication can be handled via user and password approach. In this case, the following configurations are required by the sink:
connect.hive.security.kerberos.user = jsmith
connect.hive.security.kerberos.password=password123
connect.hive.security.kerberos.krb5=/path/to/the/krb5
connect.hive.security.kerberos.jaas=/path/to/the/jaas
Configurations¶
The Kafka Connect framework requires the following in addition to any connectors specific configurations:
| Config | Description | Type | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
name |
Name of the connector | string | This must be unique across the Connect cluster |
tasks.max |
The number of tasks to scale output | int | 1 |
connector.class |
Name of the connector class | string | com.landoop.streamreactor.connect.hive.source.HiveSourceConnector |
Connector Configurations¶
| Config | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
connect.hive.kcql |
Kafka connect query language expression | string |
connect.hive.database.name |
Sets the database name | string |
connect.hive.hive.metastore |
Protocol used by the hive metastore | string |
connect.hive.hive.metastore.uris |
URI to point to the metastore | string |
connect.hive.fs.defaultF |
HDFS Filesystem default uri | string |
Optional Configurations¶
| Config | Description | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
transforms |
Aliases for the transformations to be applied to records. | string | |
config.action.reload |
Reload Action | string | RESTART |
errors.retry.timeout |
Retry Timeout for Errors | int | 0 |
errors.retry.delay.max.ms |
Maximum Delay Between Retries for Errors | int | 60000 |
errors.tolerance |
Error Tolerance | string | none |
errors.log.enable |
Log Errors | boolean | false |
errors.log.include.messages |
Log Error Details | boolean | false |
connect.progress.enabled |
Enables the output for how many
records have been processed
|
boolean | false |
connect.hive.security.kerberos.enabled |
If set to true it indicates
Kerberos is used for authentication when connecting to your cluster
|
string | none |
connect.hive.security.kerberos.auth.mode |
The authentication mode for Kerberos.
It can be KEYTAB or USERPASSWORD
|
string | none |
connect.hive.security.principal |
The principal to use for the Kerberos
connection. Used when auth.mode is set to KEYTAB
|
string | none |
connect.hive.security.keytab |
The path to the keytab file to use
to authenticate the principal when connecting to your cluster.
Used when auth.mode is set to KEYTAB
|
string | none |
connect.hive.security.namenode.principal |
The principal for HDFS Namenode.
Used when auth.mode is set to KEYTAB
|
string | none |
connect.hive.security.kerberos.user |
The user name to login to Kerberos.
Used when auth.mode is set to USERPASSWORD
|
string | none |
connect.hive.security.kerberos.password |
The user password to login to Kerberos.
Used when auth.mode is set to USERPASSWORD
|
string | none |
connect.hive.security.kerberos.krb5 |
The path to the KRB5 file.
Used when auth.mode is set to USERPASSWORD
|
string | none |
connect.hive.security.kerberos.jaas |
The path to the JAAS file.
Used when auth.mode is set to USERPASSWORD
|
string | none |
connect.hive.security.kerberos.ticket.renew.ms |
The period in milliseconds to
renew the Kerberos ticket
|
string | none |
Example¶
name=hive-source-example
connector.class=com.landoop.streamreactor.connect.hive.source.HiveSourceConnector
tasks.max=1
topics=hive_topic
key.converter=org.apache.kafka.connect.json.JsonConverter
key.converter.schemas.enable=false
value.converter=org.apache.kafka.connect.json.JsonConverter
value.converter.schemas.enable=false
connect.hive.kcql=insert into hive_topic select * from cities
connect.hive.database.name=hive_connect
connect.hive.hive.metastore=thrift
connect.hive.hive.metastore.uris=thrift://hive-metastore:9083
connect.hive.fs.defaultFS=hdfs://namenode:8020
Schema Evolution¶
Upstream changes to schemas are handled by Schema registry which will validate the addition and removal or fields, data type changes and if defaults are set. The Schema Registry enforces AVRO schema evolution rules. More information can be found here.
Kubernetes¶
Helm Charts are provided at our repo, add the repo to your Helm instance and install. We recommend using the Landscaper to manage Helm Values since typically each Connector instance has its own deployment.
Add the Helm charts to your Helm instance:
helm repo add landoop https://lensesio.github.io/kafka-helm-charts/
TroubleShooting¶
Please review the FAQs and join our slack channel